Solar system definition
The solar system is the collection of celestial objects that orbit around the Sun. It consists of the Sun, eight planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune), dwarf planets (such as Pluto), moons, asteroids, comets, and other objects such as the Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud. The solar system is located in the Milky Way galaxy.
Solar system diagram in animation (gif)
solar system facts
● The Solar System formed about 4.5 billion years ago and was formed from a dense cloud of interstellar dust and gas.
● The cloud is supposed to have collapsed when a nearby star (called Supernova) exploded and created shockwaves.
● After collapsing, this dust cloud was reduced to a solar nebula (a swirling and spinning disk of material).
● Due to gravity at the center, more and more material got pulled inside which increased the pressure at the core.
● The smaller leftover pieces became comets, meteoroids, asteroids, and small irregular moons.
● The Solar System is our neighbourhood in space. It is a collection of planets and smaller objects, all travelling around a central star, the sun. The sun is a vast ball of glowing hot gas.
● The smallest planet is Mercury and the biggest is Jupiter. Uranus is the coldest and Venus is the hottest planet.
● The hottest planet is Venus with an average temperature of 480°C and the coldest planet is Uranus with an average temperature -224°C. By comparison Earth’s average temperature is 15°C.
● The solar system is part of the Milky Way. There are at least between 250 to 500 billion stars in our Milky Way galaxy – there might even be more. That’s at least 30 times more stars in The Milky Way than there are people on Earth.
● All of the planets in the solar system orbit the sun. Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are called 'terrestrial planets'. They are mostly made of rock and metal. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are called 'gas giants'. They are mostly composed of gas with no solid surface and they have rings.
● A huge system of stars is called a galaxy and our planetary system exists on the outer spiral arm of the galaxy called the Milky Way.
● The star in our solar system is the Sun and our solar system consists of the Sun and everything else that is bound by gravity to the Sun. There are many other thousands of planetary systems apart from ours that exist in the Milky Way and orbit around their own stars
● More than 200 moons exist in the solar system, and Mercury and Venus are the only two planets that do not have a moon. Jupiter and Saturn have the maximum number of moons.
Planets Detail List With Pictures
| Planets | Planets Pictures | Distance from Sun | Planets Diameter | Planets Moons | Planets Type | Rotation Direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury | 36 million miles (57.9 million km) ( | 3,032 miles (4,880 km) | 0 | Terrestrial planet | Counter clockwise | |
| venus | 67 million miles (108 million km) | 7,521 miles (12,104 km) | 0 | Terrestrial planet | Clockwise | |
| Earth | 93 million miles (149.6 million km) | 7,917 miles (12,742 km) | 1 | Terrestrial planet | Counter clockwise | |
| Mars | 142 million miles (228 million km) | 4,212 miles (6,792 km) | 2 | Terrestrial planet | Counter clockwise | |
| Jupiter | 484 million miles (778 million km) | 86,881 miles (139,822 km) | 80 | Gas Giant | Counter clockwise | |
| Saturn | 886 million miles (1.43 billion km) | 72,400 miles (116,460 km) | 83 | Gas Giant | Counter clockwise | |
| Uranus | 1.78 billion miles (2.87 billion km) | 31,118 miles (50,724 km) | 27 | Ice Giant | Clockwise | |
| Neptune | 2.8 billion miles (4.5 billion km) | 30,761 miles (49,244 km) | 14 | Ice Giant | Counter clockwise |
Definition,Specification and facts of Sun and Planets
► What is the Sun?
The Sun is a star located at the center of the solar system. It is a giant ball of hot plasma that provides light, heat, and energy to the planets and other objects that orbit around it. The Sun is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium and is powered by nuclear reactions that convert hydrogen into helium. It is the largest object in the solar system and makes up approximately 99.86% of the total mass of the solar system. The Sun's intense energy drives the Earth's climate and weather patterns, and it is essential for life on our planet. Sun animation with description in gif
► Specification of sun
Here are some specifications of the Sun: ► Facts of sun
Here are some interesting facts about the Sun: ► What is Mercury?
Mercury is the smallest planet in our solar system and the closest planet to the Sun. It is a terrestrial planet, meaning it is composed primarily of rock and metal, with a thin atmosphere composed mainly of helium and hydrogen. The surface of Mercury is heavily cratered and rocky, with deep, steep-walled canyons called "scarps." Mercury has no moons and has the shortest rotation period of any planet in our solar system, taking about 58.65 Earth days to complete one rotation on its axis, while its orbit around the Sun takes about 87.97 Earth days. Mercury's proximity to the Sun makes it extremely hot on its sun-facing side, with temperatures that can reach over 430°C (800°F), while the side facing away from the Sun can be extremely cold, dropping to below -180°C (-290°F). Mercury animation with description in gif ► Specification of Mercury
Here are some specifications of Mercury: ► Facts of Mercury
Here are some interesting facts about Mercury: ► What is Venus?
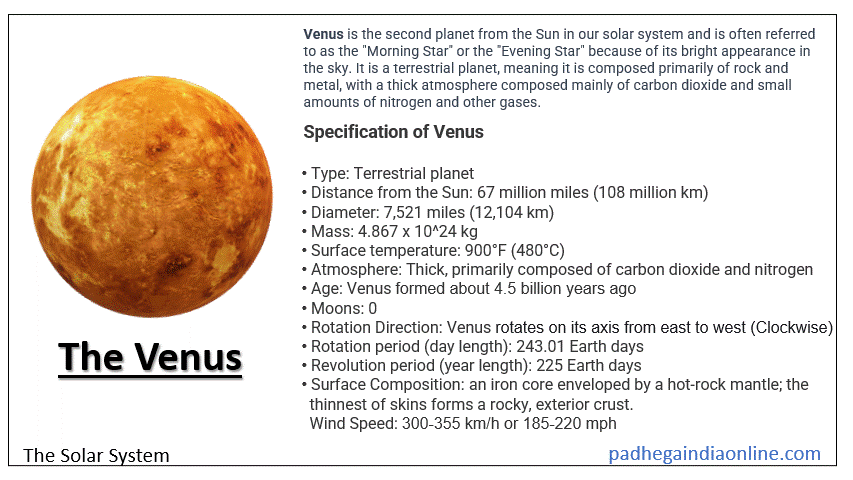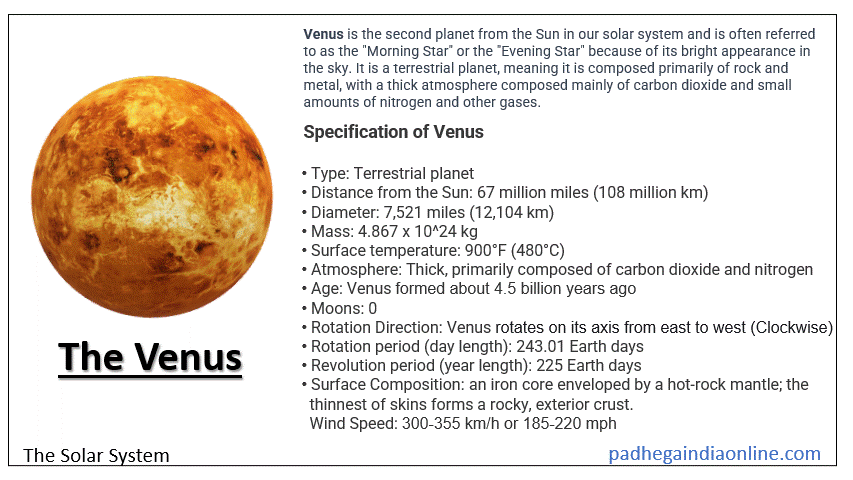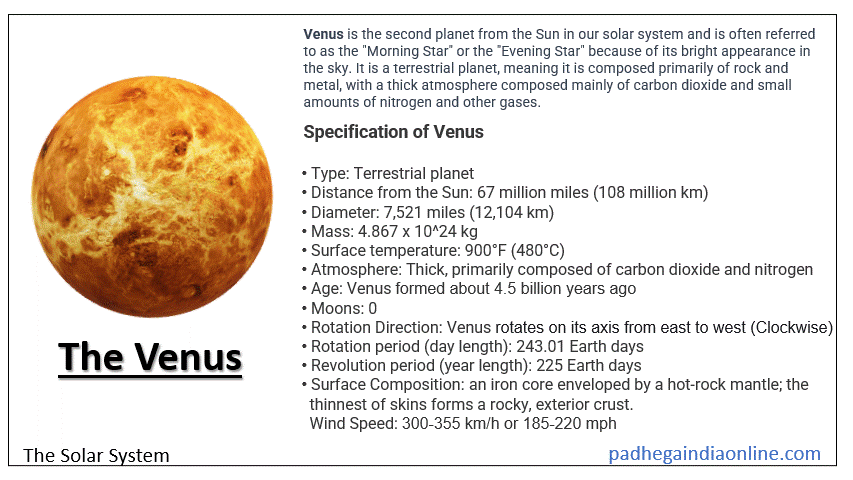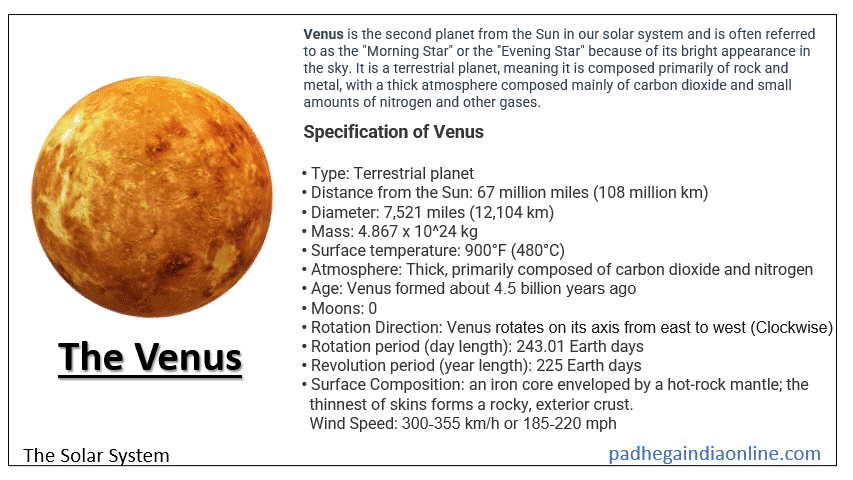
Venus is the second planet from the Sun in our solar system and is often referred to as the "Morning Star" or the "Evening Star" because of its bright appearance in the sky. It is a terrestrial planet, meaning it is composed primarily of rock and metal, with a thick atmosphere composed mainly of carbon dioxide and small amounts of nitrogen and other gases. The surface of Venus is dry and hot, with temperatures that can reach 480°C (900°F) due to a runaway greenhouse effect caused by the thick atmosphere trapping heat. Venus is covered in volcanic plains, mountains, and vast plateau regions. Venus has no moons and has the longest rotation period of any planet in our solar system, taking 243 Earth days to complete one rotation on its axis, while its orbit around the Sun takes about 225 Earth days. Venus is one of the brightest objects in the sky and has been observed by humans for thousands of years. Venus animation with description in gif ► Specification of Venus
Here are some specifications of Venus: ► Facts of Venus
Here are some interesting facts about Venus: ► What is Earth?
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and is the only known planet in the universe that has active plate tectonics, liquid water on its surface, and an atmosphere that can support life. It is a terrestrial planet, meaning it is composed primarily of rock and metal, with a relatively thin atmosphere that is composed mainly of nitrogen, oxygen, and trace amounts of other gases. Earth has a diverse and complex environment, with vast oceans, continents, mountains, and forests. Almost three quarters of Earth’s surface (about 71%) is covered in water.It is the largest of the inner planets in our solar system and has a strong magnetic field that protects it from the harmful solar wind. Earth has a single, large natural satellite, the Moon, which orbits around it. It takes about 23.9 hours for Earth to rotate once on its axis, creating day and night, and about 365.24 days to complete one orbit around the Sun, creating the length of a year. The atmosphere of Earth supports a diverse range of life, from microorganisms to complex organisms such as plants and animals, and humans. Earth animation with description in gif ► Specification of Earth
Here are some specifications of Earth: ► Facts of Earth
Here are some interesting facts about Earth: ► What is Mars?
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in our solar system. Mars is known as the "Red Planet" because iron minerals in the Martian soil oxidize, or rust, causing the soil and atmosphere to reddish appearance in the sky. It is a terrestrial planet, meaning it is composed primarily of rock and metal, with a thin atmosphere composed mainly of carbon dioxide (CO2), argon (Ar), nitrogen (N2), and a small amount of oxygen and water vapour. Mars has a dry and barren landscape, with a dusty and rocky surface that is marked by impact craters, volcanoes, and canyons. The largest volcano in the solar system, Olympus Mons, is located on Mars. Mars has two small, irregularly shaped moons, Phobos and Deimos. Many missions have been sent to Mars, including the recent Perseverance rover, which landed on the planet in February 2021 and is searching for signs of ancient microbial life and collecting samples to bring back to Earth. Mars animation with description in gif ► Specification of Mars
Here are some specifications of Mars: ► Facts of Mars
Here are some interesting facts about Mars: ► What is Jupiter?
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet in our solar system. It is a gas giant planet, meaning it is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, with small amounts of other elements. Jupiter has a thick atmosphere that is divided into several distinct bands of clouds, which are made up of ammonia, water vapor, and other compounds. Jupiter has a small rocky core, but most of its mass is in its atmosphere. The planet is also known for its Great Red Spot, a giant storm that has been raging for centuries. Jupiter has a strong magnetic field and a large system of 80 moons. The four largest moons of Jupiter, called the Galilean moons after their discoverer, include Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto, and they are some of the most interesting and active objects in the solar system. Jupiter was named after the king of the Roman gods, and it has been known since ancient times. It has been visited by several spacecraft, including the Galileo mission, which orbited the planet from 1995 to 2003 and provided detailed information about Jupiter's atmosphere, moons, and magnetic field. Jupiter animation with description in gif ► Specification of Jupiter
Here are some specifications of Jupiter: ► Facts of Jupiter
Here are some interesting facts about Jupiter: ► What is Saturn?
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest planet in our solar system. It is a gas giant planet, similar in composition to Jupiter, with a thick atmosphere of hydrogen and helium, and a small, rocky core. Saturn is also known for its prominent and extensive ring system, which is made up of billions of individual particles of rock and ice. Saturn is one of the most recognizable planets in our solar system due to its unique and beautiful ring system. It is also home to dozens of moons, including the second-largest moon in our solar system, Titan, which has a thick atmosphere and a landscape with lakes, rivers, and mountains. Saturn is named after the Roman god of agriculture and wealth, and it has been known since ancient times. It is a popular target for space exploration, with several missions having been sent to study its rings, atmosphere, and moons. Saturn animation with description in gif ► Specification of Saturn
Here are some specifications of Saturn: ► Facts of Saturn
Here are some interesting facts about Saturn: ► What is Uranus?
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun and is the third-largest planet in our solar system. It is an ice giant planet, with an atmosphere primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, as well as methane, which gives the planet its blue-green color. Uranus has a small rocky core surrounded by a thick layer of icy material. It is also unique among the planets in our solar system in that its rotation axis is tilted at an extreme angle, causing it to essentially roll on its side as it orbits the Sun. Uranus has 27 known moons, the largest of which is called Titania. Uranus also has a faint ring system made up of particles of ice and dust. Uranus was discovered in 1781 by the astronomer William Herschel and was named after the Greek god of the sky, Ouranos. It has been visited by only one spacecraft, Voyager 2, which flew by the planet in 1986 and provided the most detailed information about Uranus to date. Uranus animation with description in gif ► Specification of Uranus
Here are some specifications of Uranus: ► Facts of Uranus
Here are some interesting facts about Uranus: ► What is Neptune?
Neptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in our solar system. It is the fourth-largest planet by diameter and the third-largest by mass. Neptune is an ice giant planet, meaning it is primarily composed of materials such as water, methane, and ammonia, which are compressed into a dense liquid by the planet's strong gravity. The planet's atmosphere is mostly composed of hydrogen and helium, with small amounts of methane, which give it a blue color. Neptune has a rocky core surrounded by an icy mantle, and it has a ring system and 14 known moons. The largest of Neptune's moons is Triton, which is thought to be a captured Kuiper Belt object. Neptune was discovered in 1846 by the French astronomer Urbain Le Verrier, who predicted its location based on observed perturbations in the orbit of Uranus. It is named after the Roman god of the sea, Neptune. Like Uranus, Neptune has only been visited by one spacecraft, Voyager 2, which flew by the planet in 1989 and provided the most detailed information about Neptune to date. Neptune animation with description in gif ► Specification of Neptune
Here are some specifications of Neptune: ► Facts of Neptune
Here are some interesting facts about Neptune:
● Type: G-type main-sequence star (G dwarf star).
● Mass: 1.989 x 10^30 kilograms
● Diameter: 1.391 million km.
● Surface temperature: 5,500°C
● Core temperature: 15 million°C
● Luminosity (total amount of energy emitted): 386 billion megawatts (3.86 x 10^33 erg/s).
● Age: Sun formed about 4.6 billion years ago.
● Distance from Earth: 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles).
● Composition: Hydrogen (74.9%), Helium (24.0%), and trace amounts of other elements.
● Rotation Direction: Sun rotates on its axis from west to east (Counterclockwise)
● Rotation period: 25-36 days at the equator, up to 36 Earth-days near the poles.
● Magnetic field: Approximately 50 gauss.
● The Sun is a star, but it is much larger than most other stars in the universe.
● The Sun is located at the center of the solar system and is responsible for the majority of the light and heat that reaches Earth.
● The Sun's energy is produced by nuclear reactions that take place in its core, where hydrogen atoms are converted into helium.
● The Sun is about 4.6 billion years old, a yellow dwarf star and is thought to have another 5 billion years or so before it begins to cool and eventually becomes a white dwarf star.
● The Sun is about 93 million miles (150 million kilometers) from Earth and it’s our solar system’s only star. Without the Sun’s energy, life as we know it could not exist on our home planet (Earth).
● The sun takes about 230 million years for the Sun to make one complete trip around the Milky Way.
●The Sun is classified as a G-type main-sequence star, meaning it is in the stable phase of its life cycle.
● The Sun's surface temperature is approximately 5,500°C (9932°F), while its core temperature is estimated to be around 15 million°C (27 million°F).
● The Sun rotates on its axis, with a period that varies from 25-36 days at the equator to up to 36 Earth-days near the poles.
● The Sun has a strong magnetic field that affects the behavior of charged particles in the solar system, including the formation of sunspots and solar flares.
● The Sun is the closest star to Earth and is essential for life on our planet, as it provides the energy needed for photosynthesis in plants, which is the base of the food chain for many other organisms.
● The closest planet to the Sun is Mercury, and the farthest away is Neptune.
● The earth could fit inside the sun more than 1 million times.
● The sun is by far the biggest and heaviest object in the whole solar system, and its gravity keeps everything else travelling around it in slightly flattened circular paths called orbits.
● Type: Terrestrial planet.
● Distance from the Sun: 36 million miles (57.9 million km)
● Diameter: 3,032 miles (4,880 km).
● Mass: 3.285 x 10^23 kg
● Surface temperature: day - 800°F (430°C), night - -290°F (-180°C)
● Atmosphere: Thin, primarily composed of oxygen, sodium, hydrogen, helium, and potassium.
● Age: Mercury formed about 4.5 billion years ago
● Moons: 0
● Rotation Direction: Mercury rotates on its axis from west to east (Counterclockwise)
● Rotation period (day length): 58.65 Earth days.
● Revolution period (year length): 87.97 Earth days.
● Surface Composition: A central core, a rocky mantle, and a solid crust.
● Magnetic field: Weak, approximately 1% of Earth's magnetic field.
● Mercury is the smallest planet in our solar system, with a diameter of just 4,880 kilometers (3,032 miles).
● Despite its small size, Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun, making a complete orbit around the Sun every 87.97 Earth days.
● Mercury is the fastest planet in our solar system – traveling through space at nearly 29 miles (47 kilometers) per second.
● Mercury has a very thin atmosphere, consisting primarily of oxygen, sodium,hydrogen,helium and potassium, and a weak magnetic field that is about 1% the strength of Earth's magnetic field.
● Mercury rotates very slowly on its axis, taking 58.65 Earth days to complete a single rotation. This slow rotation, combined with its close proximity to the Sun, means that a single day on Mercury lasts 176 Earth days.
● Mercury's surface temperature varies dramatically, with daytime temperatures reaching over 800°F (430°C) and nighttime temperatures dropping to -290°F (-180°C). Nights on Mercury are freezing cold, much colder than the coldest place on Earth.
● Mercury has no moon and there are no rings.
● The sunlight on Mercury is seven times brighter than it appears on Earth.
● The planet was named after the Roman messenger of the gods, Mercury, who was known for his speed.
● Mercury was visited by NASA's Mariner 10 spacecraft in the 1970s and more recently by the MESSENGER spacecraft, which orbited the planet from 2011 to 2015, providing new insights into its surface features, composition, and magnetic field.
● The European Space Agency and JAXA launched a joint mission to Mercury in 2018. The mission, called BepiColombo, is made up of two spacecraft. ESA built the main spacecraft, the Mercury Planetary Orbiter, and JAXA supplied the Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter and now travels in space towards Mercury which it will reach by 2025. It will orbit the planet to solve mysteries about Mercury.
● Type: Terrestrial planet.
● Distance from the Sun: 67 million miles (108 million km)
● Diameter: 7,521 miles (12,104 km).
● Mass: 4.867 x 10^24 kg
● Surface temperature: 900°F (480°C)
● Atmosphere: Thick, primarily composed of carbon dioxide and nitrogen.
● Age: Venus formed about 4.5 billion years ago
● Moons: 0
● Rotation Direction: Venus rotates on its axis from east to west (Clockwise)
● Rotation period (day length): 243.01 Earth days.
● Revolution period (year length): 225 Earth days.
● Surface Composition: an iron core enveloped by a hot-rock mantle; the thinnest of skins forms a rocky, exterior crust.
● Wind Speed: 300-355 km/h or 185-220 mph
● Venus is the second planet from the Sun in our solar system and is sometimes referred to as Earth's twin due to its similar size and proximity to the Sun.
● Venus has a thick, toxic atmosphere consisting primarily of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, which creates a strong greenhouse effect, making it the hottest planet in the solar system.
● The surface temperature on Venus can reach over 800°F (480°C).
● The surface of Venus is obscured by a layer of sulfuric acid clouds, which is of yellowish color and the planet's thick atmosphere has made it difficult for spacecraft to study the planet's surface.
● Venus rotates very slowly on its axis, in the opposite direction from most other planets, with a rotation period of 243 Earth days. This means a single day on Venus is longer than a single year on Venus.
● Venus has no moons or rings.
● The surface of Venus is heavily cratered and has extensive volcanic activity, including large shield volcanoes and extensive lava flows.
● The surface of Venus hosts thousands of volcanoes, craters and super-high mountain ranges.
● Venus was named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty.
● Venus is the brightest object in the sky after the Sun and the Moon and is often referred to as the Morning Star or the Evening Star due to its appearance in the morning or evening sky.
● Several missions have been sent to study Venus, including the Soviet Venera missions in the 1970s and 1980s and the European Space Agency's Venus Express mission in the 2000s, providing valuable insights into the planet's climate and geological history.
● NASA’s Magellan spacecraft, which ended a five-year mission to Venus in 1994, mapped the broiling surface using radar. Magellan saw a land of extreme volcanism. The orbiter saw a relatively young surface, one recently reshaped (in geologic terms), and chains of towering mountains.
● Type: Terrestrial planet.
● Distance from the Sun: 93 million miles (149.6 million km)
● Distance from the Moon: 238,855 miles (384,400 km).
● Diameter: 7,917 miles (12,742 km).
● Mass: 5.97 x 10^24 kg
● Surface temperature: -88°F to 136°F (-67°C to 58°C).
● Atmosphere: Nitrogen (78%), Oxygen (21%), other gases (1%).
● Age: Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago
● Moons: 1 (Moon)
● Rotation Direction: Earth rotates on its axis from west to east (Counterclockwise)
● Rotation period (day length): 23.9 hours.
●Revolution period (year length): 365.25 days (which counts one year as 365 days).
● Surface Composition: an inner core at the planet's center, enveloped by the outer core, mantle, and crust.
● Wind Speed: 120-305 km/h or 75-190 mph
● Earth is the third planet from the Sun in our solar system and is the only known planet capable of supporting life.
● Earth is made of rock and is the only planet where water is liquid. Almost three quarters of Earth’s surface (about 71%) is covered in water.
● Earth has a diameter of 12,742 km (7,917 miles) and a mass of 5.97 x 10^24 kg, making it the fifth largest planet in the solar system.
● The Sun is 93 million miles from the Earth. The light from the Sun only takes 8 minutes to travel to the Earth.
● Earth has a diverse atmosphere, composed primarily of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), and 1 percent other gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, and neon-—the perfect balance to breathe and live., which protects life on Earth from harmful solar and cosmic radiation.
● Earth has one natural satellite, the Moon, which is the fifth largest moon in the solar system and plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability of Earth's axial tilt and regulating its ocean tides.
● The Moon is an average of 238,855 miles (384,400 kilometers) away from Earth.
● Earth rotates on its axis once every 23.9 hours, which causes the daily cycle of day and night. It revolves around the Sun once every 365.25 days, which defines the length of a year.
● Earth is divided into several distinct spheres, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and geosphere, which interact to create a complex and dynamic planet.
● The inner core is a solid sphere made of iron and nickel metals about 759 miles (1,221 kilometers) in radius. There the temperature is as high as 9,800 degrees Fahrenheit (5,400 degrees Celsius).
● Earth is home to a rich diversity of life, including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms, which have evolved over billions of years and interact to create complex ecosystems.
● Earth has a magnetic field, which helps protect life on Earth from harmful solar and cosmic radiation and also affects the planet's climate and weather patterns.
● Earth is constantly changing, with processes such as plate tectonics, erosion, and volcanic activity, which shape its surface and create a dynamic and evolving planet.
● The name of the planet “Earth” is more than 1000 years old. While all the planets are named after Greek Goddesses and Gods, Earth has its origin in Germanic language and it means “the ground.
● Type: Terrestrial planet.
● Distance from the Sun: 142 million miles (228 million km).
● Diameter: 4,212 miles (6,792 km).
● Mass: 6.39 x 10^23 kg
● Surface temperature: -225°F to 70°F (-153°C to 20°C).
● Atmosphere: Carbon dioxide (95.3%), Nitrogen (2.7%), Argon (1.6%).
● Age: Mars formed about 4.5 billion years ago
● Moons: 2 (Phobos and Deimos)
● Rotation Direction: Mars rotates on its axis from west to east (Counterclockwise)
● Rotation period (day length): 24.6 hours.
● Revolution period (year length): 687 Earth days.
● Surface Composition: a central core, a rocky mantle, and a solid crust.
● Wind Speed: 400-480 km/h or 250-300 mph
● Mars is often referred to as the "Red Planet" due to its reddish appearance in the night sky, which is caused by iron oxide (rust) on its surface.
● Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in our solar system and is a small, rocky planet with a thin atmosphere.
● Mars has a diameter of 6,792 km (4,212 miles) and a mass of 6.39 x 10^23 kg, making it the second smallest planet in the solar system after Mercury.
● Sunlight takes 13 minutes to travel from the Sun to Mars.
● Mars takes 687 days to complete its orbit of the Sun and the average temperature is -63°C.
● We could jump three times higher on Mars than you can on Earth due to the planet’s weaker gravity.
● The sunset on Mars appears blue.
● Mars has a thin atmosphere, composed primarily of carbon dioxide (95.3%), nitrogen (2.7%), and argon (1.6%), which provides limited protection from solar and cosmic radiation.
● Mars and Earth have the same similarities. Both planets have seasons, and both have layers of ice at their north and south poles. However, unlike Earth, the surface of Mars is cold and dry, with only a thin atmosphere that is mostly made up of carbon dioxide gas.
● Mars has a history of water on its surface, including dried-up riverbeds, valleys, and minerals that form in the presence of water, suggesting that liquid water may have existed on the planet in the past.
● The planet was named after the Roman god of the war because its reddish color was reminiscent of blood.
● Mars has two small moons, Phobos and Deimos, which are thought to be captured asteroids.
● There are no rings around Mars.
● Mars has a history of water on its surface, including dried-up riverbeds, valleys, and minerals that form in the presence of water, suggesting that liquid water may have existed on the planet in the past.
● The largest peak on the red planet(Mars) is a volcano called Olympus Mons, which is three times higher than Mount Everest, the highest mountain on Earth. 'Mons' is the Latin word for mountain.
● Mars has the largest volcano (Olympus Mons) and the deepest canyon (Valles Marineris) in the solar system.
● Mars has a relatively weak magnetic field, which provides limited protection from solar and cosmic radiation.
● Mars has a thin atmosphere, which means that the planet has a much colder and drier climate than Earth.
● Mars is of great interest to scientists and space agencies due to its potential to host life and its proximity to Earth, making it a prime candidate for future human exploration.
● Mars has been the subject of numerous missions by space agencies from around the world, including NASA and the European Space Agency, to study its geology, climate, and potential for life.
● Mars is the only planet where rovers were sent to explore this alien landscape. At present NASA has deployed two rovers (Perseverance, Curiosity), one helicopter (ingenuity), and one lander (Insight) for exploring the Mars surface.
● There are two rovers on the surface of Mars and six spacecraft orbiting Mars that are tasked with discovering the presence of water and searching for evidence of previous ancient life, amongst other things.
● Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), India's first interplanetary mission to planet Mars was launched onboard PSLV-C25 on November 05, 2013. ISRO has become the fourth space agency to successfully send a spacecraft to Mars orbit. Though the designed mission life is 6 months, MOM completed 7 years in its orbit on Sept 24, 2021.
● The study of Mars, including its geology, climate, and potential for life, is known as Martian Science, and is a major field of research in planetary science.
● Type: Gas Giant.
● Distance from the Sun: 484 million miles (778 million km)
● Diameter: 86,881 miles (139,822 km).
● Mass: 1.898 x 10^27 kg
● Surface temperature: -145°C to -108°C
● Atmosphere: Hydrogen (89.8%), Helium (10.2%), trace gases.
● Age: Jupiter formed about 4.5 billion years ago
● Moons: 80 moons (including the Galilean moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, Callisto).
● Rotation Direction: Jupiter rotates on its axis from west to east (Counterclockwise)
● Rotation period (day length): 9 hours and 56 minutes.
● Revolution period (year length): 11.86 Earth years.
● Surface Composition: as a gas giant, doesn’t have a true surface.
● Wind Speed: 465-545 km/h or 290-340 mph.
● Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system, It is more than 1300 times the volume of Earth ( 1,321 Earths can fit inside Jupiter), with a diameter of 139,822 km (86,881 miles) and a mass of 1.898 x 10^27 kg.
● Jupiter is a gas giant, composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, with a relatively small, rocky core.
● Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and has a strong magnetic field and a dense atmosphere.
● Jupiter is home to several famous features, including the Great Red Spot, a massive storm that has raged for at least 400 years, and the Galilean moons, four of the largest moons in the solar system (Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto).
● Jupiter has the shortest day of any planet in the solar system, rotating once every 9 hours and 56 minutes.
● Sunlight takes 43 minutes to travel from the Sun to Jupiter.
● Jupiter has the shortest day in the solar system. One day on Jupiter takes only about 10 hours (the time it takes for Jupiter to rotate or spin around once), and Jupiter makes a complete orbit around the Sun (a year in Jovian time) in about 12 Earth years (4,333 Earth days).
● Jupiter's strong gravity has helped shape the solar system by attracting and influencing the orbits of nearby asteroids, comets, and other objects.
● Jupiter also has several rings, but unlike the famous rings of Saturn, Jupiter’s rings are very faint and made of dust, not ice.
● Jupiter's atmosphere contains several unique features, including ammonia clouds, storms, and bright white ovals.
● Jupiter is named after the king of the gods in Roman mythology, while its moons are named after lovers and conquests of the god.
● Jupiter is of great interest to scientists and astronomers due to its size, composition, and dynamic weather, as well as its role as a major player in the early formation and evolution of our solar system. Several missions have been sent to Jupiter to study its atmosphere, magnetic field, and moons, and more missions are planned for the future to continue our exploration of this fascinating planet.
● There is one spacecraft currently orbiting Jupiter called Juno. Juno is trying to solve how the planet formed and finding out more about the winds that occur.
● Type: Gas Giant.
● Distance from the Sun: 886 million miles (1.43 billion km).
● Diameter: 72,400 miles (116,460 km).
● Mass: 5.683 x 10^26 kg
● Surface temperature: -178°C to -139°C
● Atmosphere: Hydrogen (96.3%), Helium (3.25%), trace gases.
● Age: Saturn formed about 4.5 billion years ago
● Moons: 83 (including Titan and Enceladus).
● Ring System: thousands of ice and rock particles in orbit around the planet.
● Rotation Direction: Saturn rotates on its axis from west to east (Counterclockwise)
● Rotation period (day length): 10 hours and 39 minutes.
● Revolution period (year length): 29.46 Earth years.
● Surface Composition: as a gas giant,Saturn doesn’t have a true surface.
● Wind Speed: 1,800 km/h or 1120 mph.
● Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and is the second-largest planet in our solar system after Jupiter.
● Saturn has a dense atmosphere, composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, and a weak magnetic field.
● Saturn is a gas giant,Saturn doesn’t have a true surface.It is composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, with Saturn's center is a dense core of metals like iron and nickel surrounded by rocky material and other compounds solidified by intense pressure and heat.
● Saturn is famous for its distinctive ring system, which is made up of millions of ice and rock particles that orbit the planet. The rings were first observed (with a telescope) in 1610 by Galileo and are made up of huge numbers of small lumps of ice and dust (mostly ice). The pieces in the rings may be as small as a millimetre or as large as a few metres across.
● Saturn's ring system extends up to 175,000 miles (282,000 kilometers) from the planet, yet the vertical height is typically about 30 feet (10 meters) in the main rings.
● Saturn takes 29.5 years to travel around the Sun.
● Named alphabetically in the order they were discovered, the rings are relatively close to each other, with the exception of a gap measuring 2,920 miles (4,700 kilometers) in width called the Cassini Division that separates Rings A and B. The main rings are A, B, and C. Rings D, E, F, and G are fainter and more recently discovered.Starting at Saturn and moving outward, there is the D ring, C ring, B ring, Cassini Division, A ring, F ring, G ring, and finally, the E ring.
● Saturn is the most distant planet that can normally be seen from Earth with the naked eye.
● Saturn is 9 times wider than Earth.
● Saturn has the longest day of any planet in the solar system, rotating once every 10 hours and 39 minutes.
● Saturn has a diameter of 116,460 km (72,400 miles) and a mass of 5.683 x 10^26 kg.
● Saturn is home to several moons, including Titan, the second-largest moon in the solar system, and Enceladus, which is of particular interest due to the presence of geysers and a subsurface ocean.
● Saturn was named after the Roman god of agriculture and wealth.
● In 2005, NASA and ESA (European Space Agency) landed a space-probe called 'Huygens' on Titan revealing the composition and the landscape of this moon. This spacecraft was part of the Cassini-Huygens that recently ended when the orbiting spacecraft Cassini was intentionally crashed into Saturn. Cassini showed us that another moon of Saturn, Enceladus is also potentially habitable.
● Type: Ice Giant.
● Distance from the Sun: 1.78 billion miles (2.87 billion km).
● Diameter: 31,118 miles (50,724 km).
● Mass: 8.681 x 10^25 kg
● Surface temperature: -224°C
● Atmosphere: Hydrogen (83%), Helium (15%), Methane (2%).
● Age: Uranus formed about 4.5 billion years ago
● Moons: 27 (including Miranda and Oberon).
● Ring System: 13 narrow rings.
● Rotation Direction: Uranus rotates on its axis from east to west (Clockwise)
● Rotation period (day length): 17 hours, 14 minutes.
● Revolution period (year length): 84.01 Earth years.
● Surface Composition: as an ice giant, Uranus doesn’t have a true surface..
● Wind Speed: 145-580 km/h or 90-360 mph
● Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun and is the third-largest planet in the solar system after Jupiter and Saturn.
● Uranus is an ice giant, composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, with a small amount of methane and traces of water and ammonia. The methane gives Uranus its signature blue color.
● Uranus was discovered in 1781 by astronomer William Herschel, although he originally thought it was either a comet or a star.
● Uranus has a diameter of 50,724 km (31,118 miles) and a mass of 8.681 x 10^25 kg, making it the third-largest planet in the solar system.
● Uranus takes 84 years to orbit the Sun and is the coldest planet, with an average temperature of -224°C.
● Uranus is a blue planet, not because of water, but because of gases that make it appear blue.
● Uranus is unique among the planets in our solar system in that it rotates on its side, meaning that its axis of rotation is nearly perpendicular to the plane of its orbit around the Sun.
● Uranus has 27 moons, including Miranda, which has a highly varied and complex surface, and Oberon, which has a heavily cratered surface.
● Uranus is about four times wider than Earth. Uranus orbits on its side, which means that its seasons are completely different to ours. Summer and winter each take 21 years at the north and south poles!
● Uranus has 13 narrow rings, which are composed of small, dark particles that are thought to be ice and dust.
● Uranus is of interest to astronomers and scientists due to its unique rotation, atmosphere, and moons, which provide insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system.
● Uranus is named after the ancient Greek god of the sky, Uranus, and was the first planet to be discovered by modern astronomers using a telescope.
● Type: Gas Giant.
● Distance from the Sun: 2.8 billion miles (4.5 billion km).
● Diameter: 30,761 miles (49,244 km).
● Mass: 1.024 x 10^26 kg
● Surface temperature: –330°F (– 201°C)
● Atmosphere: Hydrogen (80%), Helium (19%), Methane (1%).
● Age: Neptune formed about 4.5 billion years ago
● Moons: 14 (including Triton).
● Ring System: 5 faint rings.
● Rotation Direction: Neptune rotates on its axis from west to east (Counterclockwise)
● Rotation period (day length): 16 hours, 6 minutes.
● Revolution period (year length): 164.8 Earth years.
● Surface Composition: as an ice giant, Neptune doesn’t have a true surface.
● Wind Speed: 2,100 km/h or 1300 mph
● Neptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in our solar system.
● Neptune is an ice giant. Most of its mass is a hot, dense fluid of "icy" materials – water, methane and ammonia – above a small rocky core.
● Neptune was the last planet to be discovered. On the night of 23rd September 1846 astronomers discovered Neptune through a telescope.
● Neptune has a diameter of 49,244 km (30,761 miles) and a mass of 1.024 x 10^26 kg, making it the fourth-largest planet in the solar system.
● Neptune has a highly reflective atmosphere, which gives it a blue-green color, and is caused by methane absorbing red light and reflecting blue light.
● Neptune is the second coldest planet in the Solar System after Uranus, and the furthest from the Sun. Methane gas in its upper atmosphere makes it look blue in color. At the top of its cloud layers, the temperature is usually a freezing –330°F (– 201°C), though it can get even colder.
● Neptune has 14 moons, including Triton, which is the largest moon in the solar system relative to its host planet. Triton has a unique atmosphere, and its surface is covered in ice.
● The Triton moon was discovered on October 10, 1846, by William Lassell, just 17 days after Johann Gottfried Galle discovered the planet.
● Neptune is the farthest planet from the Sun. It is 30 times as far from the sun as Earth and takes 165 years to travel around the Sun. Neptune is the last of the four ‘gas giants’ and is 58 times the volume of Earth.
● Neptune has five faint rings, named Galle, Leverrier, Lassell, Arago, and Adams.The rings are made of tiny, dark particles thought to be ice and dust.
● Neptune is famous for the "Great Dark Spot," a large, rotating storm that was observed in its atmosphere by the Voyager 2 spacecraft in 1989.
● Neptune is named after the ancient Roman god of the sea, Neptune, and was the first planet to be discovered using mathematical predictions, rather than observation.